Apply for Medicare
Essential Highlights

Individuals who are already receiving Social Security Benefits at least four months prior to reaching their 65th birthday month will be enrolled in Medicare automatically.

It is recommended to sign up for Medicare during the Initial Enrollment Period, unless you meet the criteria for a Special Enrollment Period.
To enroll in Medicare, individuals have the option to submit their application through various channels including online submission via Social Security’s website, by phone, or by visiting a local Social Security office. Additionally, 411Medicare.com is available as a resource to help guide applicants through the enrollment process.

Applying for Medicare
If you’re reading this, chances are you’re nearing the age where applying for Medicare becomes a key part of your healthcare planning. As experienced insurance representatives, we’ve had the pleasure of helping many seniors navigate the world of Medicare, and we are here to make it as simple and stress-free as possible for you. Applying for Medicare might seem complex at first glance, but don’t worry—we’ll break it down together.
What is Medicare?
Let’s start with the basics. Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for people aged 65 and older. It’s also available to some younger people with disabilities and individuals with End-Stage Renal Disease. The program helps cover many healthcare costs, but it’s important to understand the different parts and what they offer.
When to Apply for Medicare
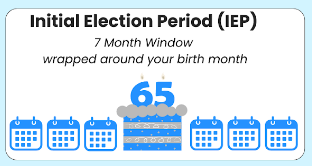
The Initial Enrollment Period is your first opportunity to sign up for Medicare. It starts three months before you turn 65, includes your birth month, and ends three months after you turn 65. This seven-month window is crucial to avoid late enrollment penalties.
Personal Tip: Mark your calendar! Many people get caught up in birthday celebrations and forget about applying for Medicare. Setting a reminder can save you from unnecessary costs later.


Special Enrollment Period (SEP)
If you’re still working and have health insurance through your employer (or your spouse’s employer), you might qualify for a Special Enrollment Period. This allows you to sign up for Medicare without penalty after your Initial Enrollment Period has ended.
General Enrollment Period (GEP)
If you miss your Initial Enrollment Period and don’t qualify for a Special Enrollment Period, you can sign up for Medicare during the General Enrollment Period, which runs from January 1 to March 31 each year. However, be aware that you may face late enrollment penalties.
How to Apply for Medicare
Step-by-Step Guide
- Determine Your Eligibility: Most people qualify for Medicare at age 65. If you’re already receiving Social Security benefits, you’ll be automatically enrolled in Parts A and B.
- Gather Necessary Documents: You’ll need your Social Security number, proof of U.S. citizenship or legal residency, and details about any current health insurance.
- Apply Online: The easiest way to apply for Medicare is through the Social Security Administration’s website. It’s quick and convenient.
- Apply by Phone or In Person: If you prefer, you can call the Social Security office or visit in person to apply.
Choosing the Right Medicare Plan
Factors to Consider
When choosing a Medicare plan, it’s important to consider your healthcare needs, budget, and lifestyle. Here are some factors to keep in mind:
- Healthcare Needs: Do you have chronic conditions that require regular doctor visits? Make sure your plan covers these services.
- Prescription Drugs: List out your medications and check if they’re covered under the plan’s formulary.
- Budget: Consider premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs. Balance these costs with the coverage benefits.
- Additional Benefits: Some Medicare Advantage plans offer extras like vision, dental, and fitness memberships.
Comparing Original Medicare vs. Medicare Advantage
Original Medicare offers flexibility in choosing healthcare providers but may come with higher out-of-pocket costs unless you have supplemental coverage. Medicare Advantage plans, on the other hand, often have lower out-of-pocket costs and additional benefits but may require you to use a network of doctors.
Medicare Supplement Policies also known as MediGap
If you choose Original Medicare, you might want to consider a Medigap policy to help cover out-of-pocket costs like copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. These plans are sold by private companies and can provide peace of mind by filling in the “gaps” in Original Medicare coverage.
Common Questions and Concerns
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What happens if I don’t sign up for Medicare Part B when I’m first eligible?
If you don’t sign up for Part B when you’re first eligible and you don’t have other credible coverage, you will have to apply during the General Enrollment Period and may have to pay a late enrollment penalty for as long as you have Part B.
Clarifying Common Misconceptions
Misconception: Medicare is free.
Reality: While Part A is usually premium-free, there are costs associated with Parts B, C, and D, including premiums, deductibles, and copayments.
Misconception: Medicare covers all healthcare costs.
Reality: Medicare helps cover many healthcare costs, but it doesn’t cover everything. There are still out-of-pocket costs for services like long-term care, dental, vision, and hearing unless you have additional coverage.
Applying for Medicare doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By understanding the different parts, knowing when to apply, and choosing the right plan for your needs, you can make informed decisions about your healthcare. Remember, it’s okay to ask for help if you need it—whether from a family member, friend, or insurance representative.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to contact us. Your health and peace of mind are important, and I’m here to help you every step of the way.
Key Details Summarized


Let Us Help you with Your Medicare Choices
Error: Contact form not found.